The Annual Increment Chart for Government Employees in Pakistan (2024), detailing the fixed salary increases across all pay scales from BPS-01 to BPS-22. Understand the factors influencing these annual increments, such as inflation, economic conditions, and government fiscal policies. Learn how these salary adjustments impact government employees’ compensation, providing insights into the wage structure within Pakistan’s public sector. Stay informed about how government decisions shape public sector salaries and the overall financial well-being of government workers in 2024.
Annual Increment Chart for Government Employees in Pakistan: 2024
The salary structure and annual increment policy for government employees play a crucial role in maintaining employee motivation, ensuring retention, and promoting long-term commitment to public service. In Pakistan, the government periodically revises salary structures and annual increments, typically through recommendations made by commissions such as the Pay and Pension Commission. These revisions are necessary to keep pace with inflation, economic conditions, and the overall financial health of the country.
Overview of the Government Salary Structure in Pakistan
In Pakistan, government employees are paid according to a defined pay scale system, which is categorized into various basic pay scales (BPS). These pay scales range from BPS-01 (the lowest) to BPS-22 (the highest). Each pay scale corresponds to a specific range of salaries, and the increments are applied accordingly. These scales are reviewed periodically by the Pay and Pension Commission, which sets the guidelines for salary adjustments, including annual increments, allowances, and other compensatory benefits.
The government of Pakistan provides annual increments to ensure that the purchasing power of government employees is maintained in line with inflation rates and to reward employees for their ongoing service. While the basic pay scale determines the base salary, other factors, such as experience, performance, and promotions, also contribute to an employee’s overall earnings.
Structure of Annual Increments for 2024
In 2024, the government of Pakistan has implemented a uniform annual increment policy, providing fixed increases to all employees in each pay scale. This increment applies to employees across all federal and provincial government departments, subject to individual performance and tenure. The increments are designed to reflect the government’s commitment to addressing inflationary pressures while maintaining a fair wage structure across all levels.

Annual Salary Increase for Government Employees (BPS-01 to BPS-22) – Effective 1st December 2024
The Government of Pakistan has announced the annual salary increment for government employees in the Basic Pay Scales (BPS-01 to BPS-22), which will take effect from 1st December 2024. This increment is designed to help employees cope with inflation and adjust their salaries in accordance with the current economic conditions. The increment will apply across all government sectors, ensuring a uniform increase in the salary of public servants.
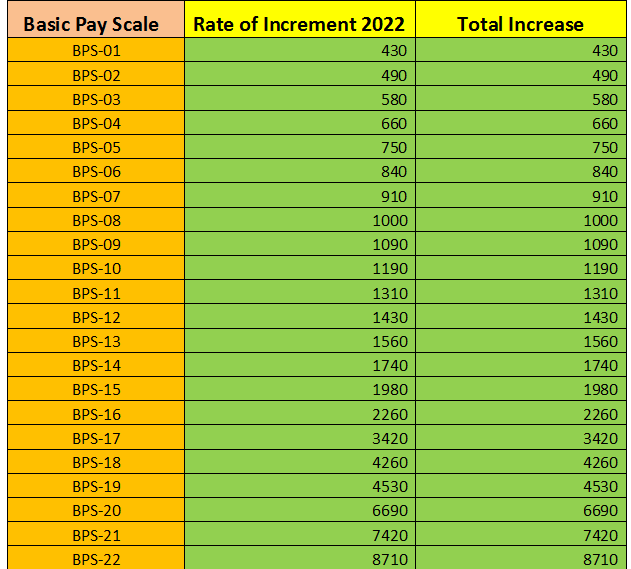
The table below shows the fixed annual increment for employees across various pay scales, from BPS-01 to BPS-22:
| Sr. No | Basic Pay Scale (BPS) | Annual Increment 2024 (Rs.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BPS-01 | 430 |
| 2 | BPS-02 | 490 |
| 3 | BPS-03 | 580 |
| 4 | BPS-04 | 660 |
| 5 | BPS-05 | 750 |
| 6 | BPS-06 | 840 |
| 7 | BPS-07 | 910 |
| 8 | BPS-08 | 1000 |
| 9 | BPS-09 | 1090 |
| 10 | BPS-10 | 1190 |
| 11 | BPS-11 | 1310 |
| 12 | BPS-12 | 1430 |
| 13 | BPS-13 | 1560 |
| 14 | BPS-14 | 1740 |
| 15 | BPS-15 | 1980 |
| 16 | BPS-16 | 2260 |
| 17 | BPS-17 | 3420 |
| 18 | BPS-18 | 4260 |
| 19 | BPS-19 | 4530 |
| 20 | BPS-20 | 6690 |
| 21 | BPS-21 | 7420 |
| 22 | BPS-22 | 8710 |
Key Points Regarding the 2024 Increment
The annual increments for 2024 reflect a consistent approach to salary increases, which ensures that government employees at all levels receive a fair adjustment based on their existing pay scales. These increments are implemented without any change in the allowances for the time being, though allowances may be revised in subsequent years.
This chart includes the basic pay, minimum basic pay, increment, and maximum pay levels for each grade.
| Grade | Basic Pay (PKR) | December Increment (PKR) | Max Pay (PKR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,550 | 430 | 26,450 |
| 2 | 13,820 | 490 | 28,520 |
| 3 | 14,260 | 580 | 31,660 |
| 4 | 14,690 | 660 | 34,490 |
| 5 | 15,230 | 750 | 37,730 |
| 6 | 15,760 | 840 | 40,960 |
| 7 | 16,310 | 910 | 43,610 |
| 8 | 16,890 | 1,000 | 46,890 |
| 9 | 17,470 | 1,090 | 50,170 |
| 10 | 18,050 | 1,190 | 53,750 |
| 11 | 18,650 | 1,310 | 57,950 |
| 12 | 19,770 | 1,430 | 62,670 |
| 13 | 21,160 | 1,560 | 62,960 |
| 14 | 22,530 | 1,740 | 74,730 |
| 15 | 23,920 | 1,980 | 83,320 |
| 16 | 28,070 | 2,260 | 95,870 |
| 17 | 45,070 | 3,400 | 113,470 |
| 18 | 56,880 | 4,260 | 142,080 |
| 19 | 87,840 | 4,530 | 178,440 |
| 20 | 102,470 | 6,690 | 196,130 |
| 21 | 113,790 | 7,420 | 217,670 |
| 22 | 122,190 | 8,710 | 244,130 |
This table outlines the revised annual pay scale increments for government employees under the federal government in 2024.
4. Factors Influencing Annual Increments
Several factors play a significant role in determining the size and structure of the annual increments for government employees in Pakistan. These include:
a) Inflation and Cost of Living
Inflation is one of the most important factors influencing salary increments. With the increasing cost of living in Pakistan, the government ensures that salary increments align with inflation to help employees maintain their purchasing power. In 2024, inflationary pressures have been a key consideration in determining the increments, although the increase may not fully offset the rising costs of goods and services.
b) Economic Conditions and Budgetary Constraints
The financial health of the government and its fiscal policies also influence how much it can afford to increase the salaries of its employees. Pakistan has faced economic challenges in recent years, including a widening fiscal deficit, which means that while increments are provided, they must be managed within the broader fiscal framework.
c) Public Sector Wage Policies
The government’s broader wage policies, as determined by the Pay and Pension Commission, help guide the structure and implementation of annual increments. The government aims to balance employee welfare with national budgetary priorities, ensuring that the pay scale system remains sustainable while being fair to public servants.
d) Recommendations of Pay Commissions
The Pay and Pension Commission regularly reviews the pay structures for government employees, and its recommendations influence decisions regarding salary revisions and annual increments. Any revisions in the coming years will likely be informed by the findings of this commission, which is tasked with ensuring equitable pay practices for all government employees.
5. Impact of Annual Increments on Government Employees
Annual increments serve several purposes for government employees in Pakistan. These include:
a) Maintaining Purchasing Power
With inflation steadily eroding the value of money, annual increments are necessary to help employees cope with rising living costs. The fixed percentage increments help ensure that employees can maintain their standard of living despite inflation.
b) Motivation and Retention
A guaranteed annual increment serves as an incentive for government employees to continue their service. It provides a sense of financial security and shows that their contributions to the public sector are valued. Regular increments also help in employee retention, as the promise of a steady pay rise encourages employees to stay within the system.
c) Fair Compensation Across All Grades
By providing increments across all basic pay scales, the government ensures that employees at every level—whether in lower, mid-level, or senior positions—receive fair compensation for their work. This helps maintain a level of equity within the public sector, preventing dissatisfaction among employees in lower pay grades.
6. Challenges and Criticisms of the Increment System
While the annual increment policy has benefits, there are certain challenges and criticisms:
a) Limited Impact on Low-Income Employees
For lower-level employees, the fixed increments may not significantly increase their purchasing power, especially in the face of high inflation. The increments may only partially offset rising costs of essentials like food, housing, and healthcare.
b) Lack of Performance-Based Adjustments
One criticism of the current increment system is the absence of performance-based salary adjustments. In many cases, employees receive the same increment regardless of their work performance. This can demotivate high-performing employees, as there is no direct financial reward for exceptional work.
c) Fiscal Constraints
Given Pakistan’s economic challenges, the government faces fiscal constraints that limit its ability to provide larger increments. Critics argue that the increments, while appreciated, may not be sufficient to address the real financial needs of employees, especially those in lower pay scales.
7. Conclusion
The annual increment chart for government employees in Pakistan for 2024 reflects the government’s ongoing effort to support public servants while managing fiscal.
